- Here are all the details about LEDs.
In electrical equipment, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are a commonly used standard light source. It may be used for many different things, from big billboard advertisements to your cell phone. They are primarily used in gadgets that display various forms of data including the time.
- LED: What is it?
A semiconductor device known as a light-emitting diode (LED) releases light when an electric current passes through it. An LED emits light when current flows through it because the electrons recombine with the holes. LEDs permit current to flow in one direction while blocking current flow in the other.
P-N junctions with heavy doping are used in light-emitting diodes. When forward biased, an LED will produce colored light at a specific spectral wavelength depending on the semiconductor material and doping level. An LED is encased in a transparent cover, as seen in the figure, to allow light to be released.
- LED Indicator
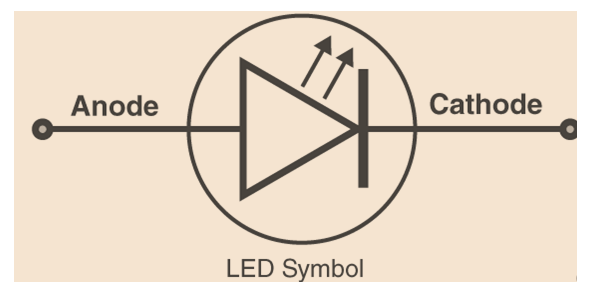
The LED symbol is a diode represented by the regular symbol plus two tiny arrows that indicate light emission.
- Basic LED Circuit
Below is a figure that depicts a basic LED circuit.
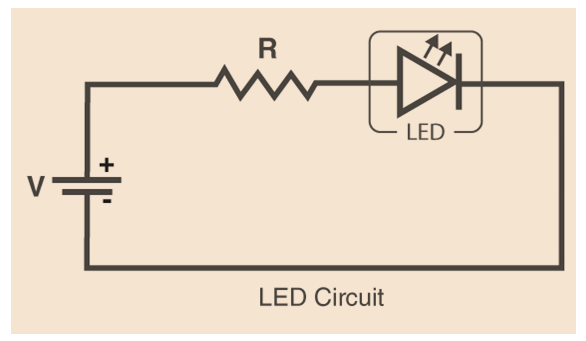
An LED, a voltage supply, and a resistor to control the current and voltage make up the circuit.
- What is the operation of an LED?
Minority electrons are transmitted from p → n and minority holes are sent from n → p in a forward biased diode. Minority carrier concentration rises at the junction boundary. At the intersection, the extra minority carriers recombine with the carriers carrying the majority charges.
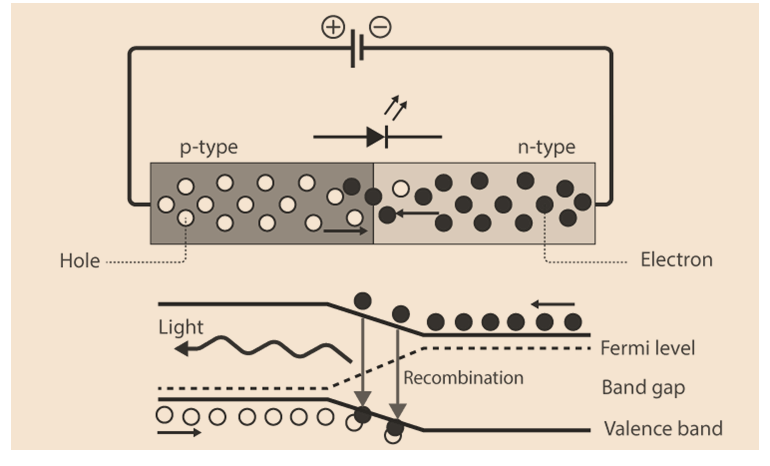
When there is recombination, the energy is released as photons. Heat is produced when energy is released in conventional diodes. However, photons are the form that the energy is emitted in light-emitting diodes. This phenomenon is known as electroluminescence. An optical and electrical phenomena known as electroluminescence occurs when a substance reacts to an electric current by releasing light. The light intensifies and reaches its maximum as the forward voltage rises.
- What factors influence an LED's color?
The semiconducting element's substance determines the color of an LED. Aluminum gallium indium phosphide and indium gallium nitride alloys are the two main materials utilized in LEDs. Red, orange, and yellow light are produced by alloys made of aluminum, and green, blue, and white light are produced by alloys made of indium. The color of the light that is emitted is altered by slight variations in the composition of these alloys.
- Characteristics of Laser Light
Laser light is coherent, directed, and monochromatic.
- Monochromatic Laser Light
Laser light is composed of just one color, as opposed to white light, which is composed of seven colors.
- The Direction of Laser Light
The light from a laser is very directed.
- Coherent Laser Light
Because the wavelengths of laser light are in phase both in space and time, laser light is coherent.
- Applications for LEDs LEDs
are used in many different industries, such as robotics, optical
communication, alarm and security systems, remote-controlled operations,
etc. Because of its durability, low power consumption, quick response
time, and quick switching capabilities, it is used in a variety of
applications. Here are some common applications for LEDs:
LEDs are utilized in displays, automobiles, TV backlighting, and light dimming technologies. - LED Types
The list of several LED kinds that are made with semiconductors is as follows:
• Tiny LEDs
Red, Green, and Blue LEDs; High-Power LEDs; Flash LEDs; Bi- and
Tri-Colored LEDs
• Lighting LED
• Alphanumeric LED
LEDs have advantages over incandescent light bulbs.
-
Compared to incandescent power lamps, LEDs have the following advantages:
• They require a low operating voltage and waste less electricity.
• There is no need for LEDs to warm up.
• They are robust and long-lasting; • The light they emit is
monochromatic.
FAQs, or frequently asked questions
Q1: What is LED technology?
A semiconductor device known as a light-emitting diode (LED) releases light when an electric current passes through it.
Q2: What is the purpose of Light Emitting Diodes?
LEDs are used in many different applications, from enormous billboards to your cell phone. They are primarily used in gadgets that display various forms of data including the time.
Q3: How do LEDs function?
LEDs operate via the electroluminescence principle. Minority and majority charge carriers recombine at the junction as current flows through the diode. Photons are released as a result of recombination. The light intensifies and reaches its maximum as the forward voltage rises.
Q4: Can you explain electroluminescence?
An optical and electrical phenomena known as electroluminescence occurs when a substance reacts to an electric current by releasing light.
Q5: What benefits do LEDs offer?
LEDs require a low operating voltage and use less power. LEDs require no warm-up period.